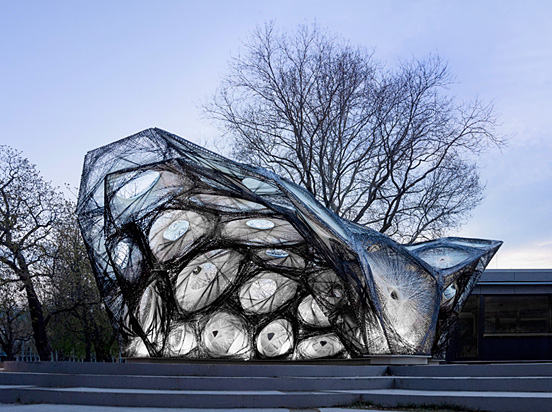
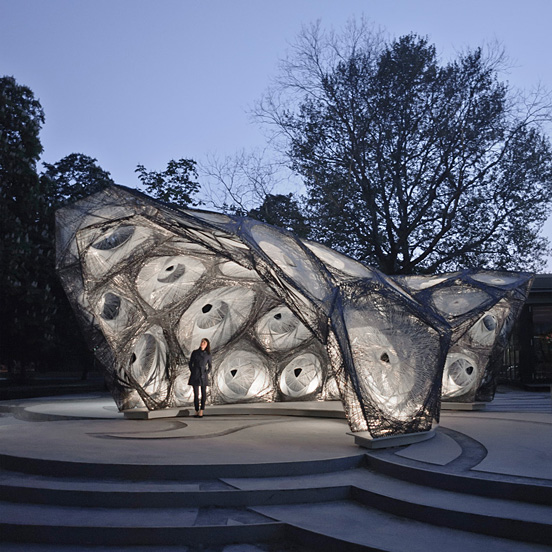
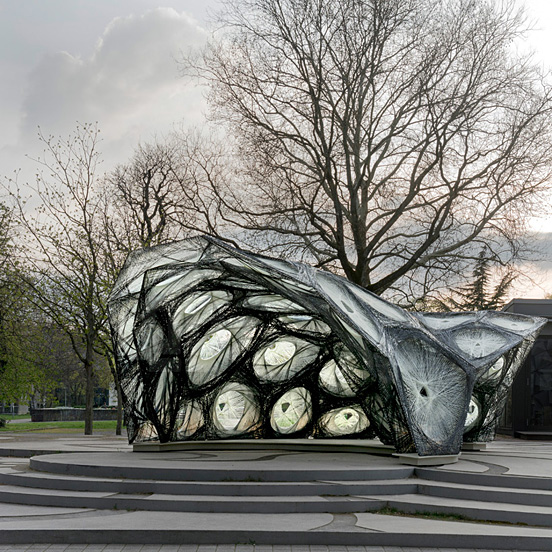
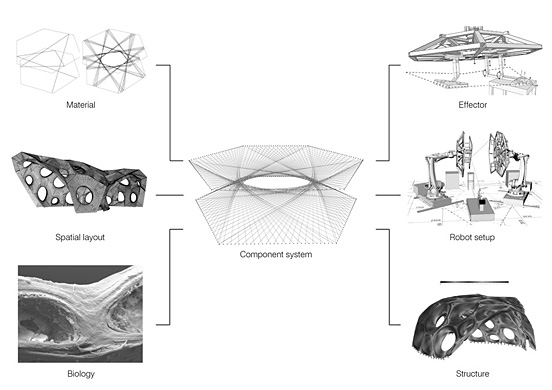
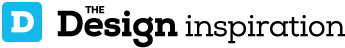The Institute for Computational Design (ICD) and the Institute of Building Structures and Structural Design (ITKE) of the University of Stuttgart have constructed another bionic research pavilion. The project is part of a successful series of research pavilions which showcase the potential of novel design, simulation and fabrication processes in architecture. The project was planned and constructed within one and a half years by students and researchers within a multi-disciplinary team of biologists, paleontologists, architects and engineers.
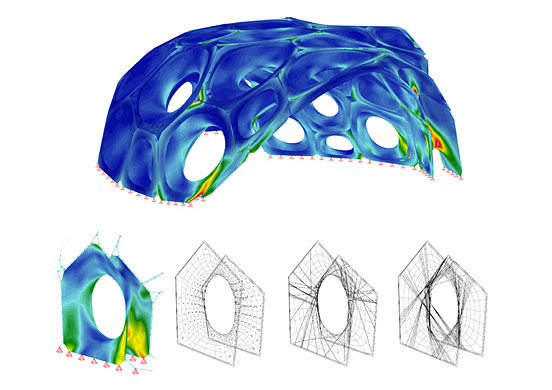
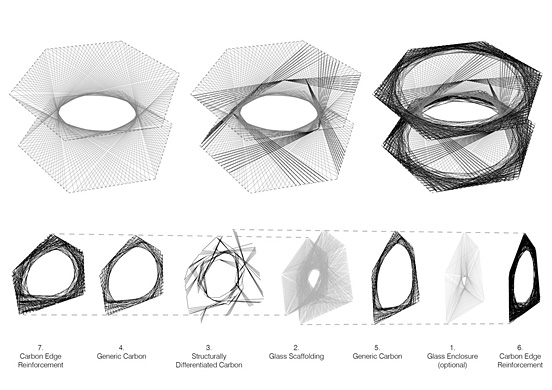
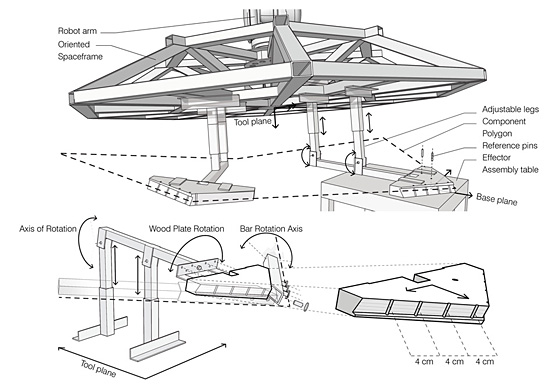
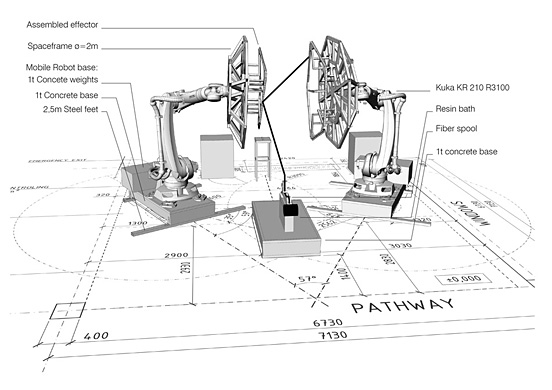
The focus of the project is a parallel bottom-up design strategy for the biomimetic investigation of natural fiber composite shells and the development of novel robotic fabrication methods for fiber reinforced polymer structures. The aim was the development of a winding technique for modular, double layered fiber composite structures, which reduces the required formwork to a minimum while maintaining a large degree of geometric freedom. Therefore, functional principles of natural lightweight structures were analyzed and abstracted in cooperation with the Institute of Evolution and Ecology and the department for Paleobiology of the University of Tübingen. Through the development of a custom robotic fabrication method, these principles were transferred into a modular prototype pavilion.